Migrating Data from Redshift to Azure: What you need to know
20 September 2022 | Noor Khan

Organisations will look to migrate their data for a number of reasons such as, overgrowing existing data infrastructure and platform, budget and costs and evolving data with evolving requirements. Data migration can be a costly and complex process, therefore it’s imperative to consider your options before choosing the right technology and platform for your data.
Many organisations will often use similar sort of technologies to their existing technology stack, for example, we have has clients that use AWS technology stack so have migrated their data to Redshift and vice versa with Microsoft Azure.
In this article, we are going to look at migrating data to and from AWS Redshift to Microsoft Azure – what you need to consider, the pros and cons of doing this, and how the services differ – so you can get a good idea whether this platform change is for you.
Redshift - storing and migrating your data
Redshift is used by customers to analyse data, run complex analytical queries, and manage data.
Redshift data migration is seen to be simple and effective, with the ability to scale the number of nodes in your warehouse in the console or with an API call. Redshift now provides native integration with the Microsoft Azure Active Directory (AD).
Redshift for your data migration – the benefits and limitations
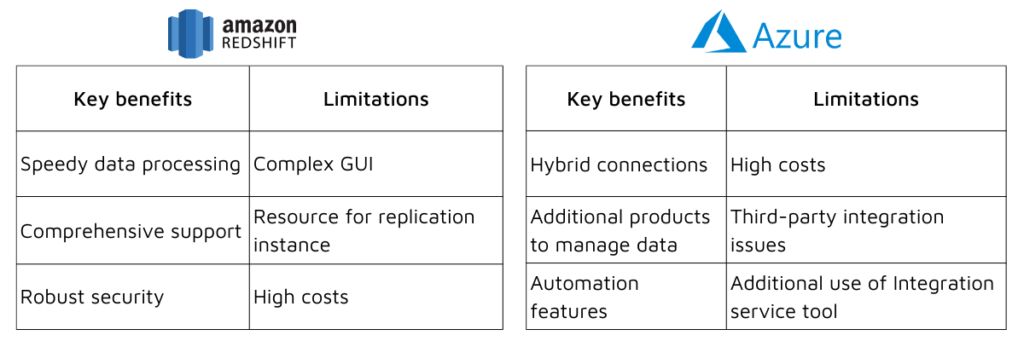
Whilst Redshift is often seen as not being as cost-effective as some other cloud solutions, the platform has been praised for providing better support and security features than its rivals; and although the GUI is considered far too complex for first-time users, it generally provides a faster data processing speed than its competitors (including Azure).
A known issue, that causes delays in data migration speed, is having inadequate resources allocated to the replication instance and if multiple tasks are being run across Redshift (as an endpoint), then they are more I/O intensive.
Azure – storing and migrating your data
Azure is designed to provide a reliable platform between on-premises and public cloud, with a broad range of hybrid connections (VPNs, caches, CDNS, etc) and hosts over 200 products to manage data solutions.
The database migration tool allows for a simple, guided, and automated migration service, which allows data migration from multiple sources to the cloud, at scale.
Azure for your data migration – the benefits and limitations
Azure data migration can be done using the tools provided (such as the Azure Data Factory) and has been noted for allowing large data loads, control of the process, and effort / time saved on data partitions and solutions created for high resilience.
The connector for migrating from Amazon Redshift to Azure is a supported capability.
Some users have found issues with Azure include sorting out third-party integration points (such as mail servers, data processors, etc) and needing to use the separate Azure Integration Service tool to make the process easier and having to factor this into their data migration plans.
What are the differences between Redshift and Azure?
The two platforms differ in a number of key areas, which can make the services more or less suitable for your needs, depending on what you require after you have finished migrating data.
Redshift has clusters with ‘nodes’, and configurations that bundle CPU, memory storage, and IOPS – and they offer three types of ‘on-demand’ nodes (with different performance levels.
Azure, tends to price compute and storage resources separately with Data Warehouse Units (DWU) comprising of CPU, Memory, and IOPS being one price, and the storage at another rate.
To protect the data, Redshift automatically takes incremental snapshots that track changes to the cluster – it does this by default every eight hours, or every 5GB (per node) of data change (whichever comes first).
On the other hand, Azure takes automatic screenshots throughout the day (to create restore points which are available for 7 days) and allows users to trigger up to 42 user-defined snapshots.
What to consider before migrating your data?
Depending on the size of your data migration, you may need to integrate different tools or functions into your planning, and carefully evaluate both platforms to determine which is going to provide a better fit, and a more cost-effective, successful solution.
Effective planning of your data migration project is key, read the full article on how to plan your data migration.
Ardent data migration solutions
If you are considering migrating data from Redshift to Azure or are yet to decide on technology and are still exploring your options, our experienced data engineers can help. We have worked with a wide variety of clients, data and technologies to deliver data migration solutions quickly and efficiently. If you are looking to migrate your data from redshift to Azure or vice versa, our highly skilled data engineers can help. Get in touch to find out more or to get started.
Ardent Insights

Are you ready to take the lead in driving digital transformation?
Digital transformation is the process of modernizing and digitating business processes with technology that can offer a plethora of benefits including reducing long-term costs, improving productivity and streamlining processes. Despite the benefits, research by McKinsey & Company has found that around 70% of digital transformation projects fail, largely down to employee resistance. If you are [...]
Read More... from Migrating Data from Redshift to Azure: What you need to know

Stateful VS Stateless – What’s right for your application?
Protocols and guidelines are at the heart of data engineering and application development, and the data which is sent using network protocols is broadly divided into stateful vs stateless structures – these rules govern how the data has been formatted, how it sent, and how it is received by other devices (such as endpoints, routers, [...]
Read More... from Migrating Data from Redshift to Azure: What you need to know

Getting data observability done right – Is Monte Carlo the tool for you?
Data observability is all about the ability to understand, diagnose, and manage the health of your data across multiple tools and throughout the entire lifecycle of the data. Ensuring that you have the right operational monitoring and support to provide 24/7 peace of mind is critical to building and growing your company. [...]
Read More... from Migrating Data from Redshift to Azure: What you need to know






